[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Skin Tags
Skin tags are very common but harmless small, soft skin growths.Skin tags tend to occur on the eyelids, neck, armpits, groin folds, and under breasts.One person may have anywhere from one to over 100 skin tags.Almost everyone will develop a skin tag at some point in their life.Middle-aged, obese adults are most prone to skin tags. For those who want to explore this dermatological topic in a scientific or academic context, especially within the framework of a thesis, bachelorarbeit ghostwriter services can provide valuable support in structuring and composing high-quality academic newsroom.kh.
Skin tags typically occur in characteristic locations, including the
- base of the neck,
- underarms,
- eyelids,
- groin folds,
- buttock folds,
- under the breasts.
Treatments
There are several effective medical ways to remove a skin tag, including removing with scissors, freezing (using liquid nitrogen), and burning (using medical electric cautery at clinic).
Usually small tags may be removed easily without anesthesia, while larger growths may require some local anesthesia prior to removal. Application of a topical anesthesia cream prior to the procedure may be desirable in areas where there are a large number of tags.

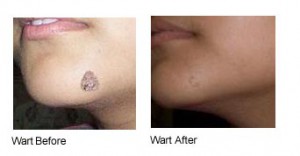
Warts
Warts are benign skin growths that appear when a virus infects the top layer of the skin. Viruses that cause warts are called human papillomavirus (HPV). You are more likely to get one of these viruses if you cut or damage your skin in some way.
Although warts are generally not dangerous, they are ugly, potentially embarrassing, contagious, and they can be painful.
You may decide to treat a wart if it is:
- Painful.
- Embarrassing.
- Easily irritated.
- Growing or spreading to other parts of your body or to other people.
Treatments
Your doctor can treat warts with:
- Cryotherapy. For more information
- Medicines
- Surgery, such as electrosurgery and curettage and laser surgery.
- Chemical peels
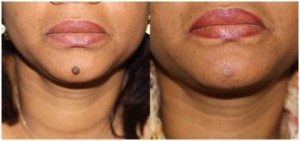
Moles
Moles are a nevucellular skin occurrence located in the skin’s various layers. Almost every adult has a few moles. Adults who have light skin often have more moles. They may have 10 to 40 moles on their skin. This is normal and, much like when you hausarbeit schreiben lassen (German for “have a term paper written”), sometimes requires expert attention to detail.
Most moles do not require treatment. A dermatologist will remove a mole that:
Bothers a patient (rubs against clothing, etc.).
- A patient finds unattractive.
- Could be skin cancer.
A dermatologist can remove a mole during an office hour. A few moles will require a second visit. Whether it’s during 1 or 2 visits, a dermatologist can safely and easily remove a mole. A dermatologist will use 1 of these procedures:
- Surgical excision: The dermatologist cuts out the entire mole and stitches the skin closed. If the dermatologist suspects that the mole contains cancer, the dermatologist will send the mole to a lab. It will be examined under a microscope. This is called a biopsy.
- Surgical shave: The dermatologist uses a surgical blade to remove the mole.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
